The different areas had to trade to get what they needed. They were ruled by the males.

West Africa And The Role Of Slavery U S History
The area of West Africa consists of the southern portion of the bulge of the continent which extends westward to the Atlantic Ocean.
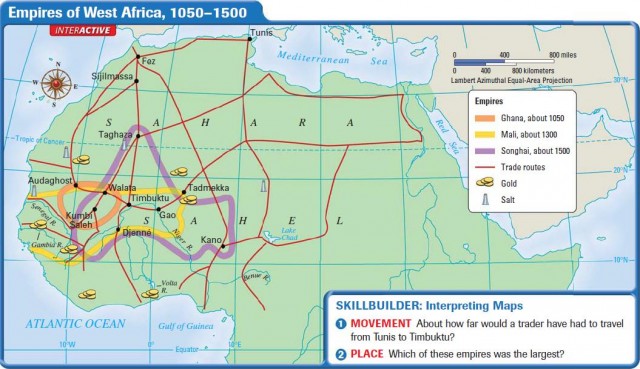
. How ever the Sahara desert was a significant barrier to travel and trade. Rivers were used to transport goods to trade. Effects on Africa As African rulers organized the capture of slaves traditions were created of brutal and arbitrary intervention by the powerful in people lives.
Trade in the metal went back to antiquity but when the camel caravans of the Sahara linked North Africa to the savannah interior the trade really took off. The geography impacted where people could live important trade resources such as gold and salt and trade routes that helped different civilizations to interact and develop. West African Geography and Regional Influences.
Historian Kathrin Kubetzek says in Atlantic Slave Trade. How did geography affect trade in West Africa. History 7 West Africa.
It became easier when camels started to be used to carry goods to trade. By Ju-Juanna Perkins. How did geography affect Africa.
The majority of the slaves were taken from West Africa. As West Africas population booms and its economy continues to expand the opportunities for businesses to trade across the region are vast. Despite this economic growth rates in most of the countries are lagging and poverty remains high.
Caravans crossing the desert could easily get lost in the drifting unmarked sands of the. How did geography affect trade in West Africa. West Africa was one of the worlds greatest producers of gold in the Middle Ages.
Identify the characteristics of Africas four geographic zones and their locations. Trade between these two regions was a natural consequence of the different environments and way of life enjoyed by the Berbers and the West African peoples who inhabited the two regions. Geography affected trade because there are so many regions in Africa with different resources.
This led to more war and more destruction of empires and civilizations. To prepare for a trip camels would be fattened up for the journey across the desert. This area is bisected by the African Transition Zone which borders the southern fringe of the Sahara Desert.
Actually the West Africa geography worked against the trans-Saharan trade. Geographical Motivations for Change. Who made the decisions in a family-based community.
The rivers were like highways but canoes were used. Donkey and horses were used to carry goods and items for trade but these animals couldnt face the heat and they eventually dies to the heat. The geography of Africa helped to shape the history and development of the culture and civilizations of Ancient Africa.
The United States of America has a moral obligation to help West African countries to continue to develop. Tribes traded things for things that they need from another tribe. A succession of great African empires rose off the back of the gold trade as salt ivory and slaves were just some of the commodities.
This region is bisected by the African Transition Zone which borders the southern edge of the Sahara Desert. Hard to trade due to the climate which was very hot and humid. The foremost bodily options embody the Sahara Desert and the Niger River.
Expansion of reliable food production the establishment and stabilization of governments the creation of control over intra- and interregional trade routes and shifts in who. The Transatlantic Slave Trade took place from the 16 th to the 19 th century and in that time between 10 and 12 million African slaves were brought to the Americas. Notably many countries are in tropical disease-prone areas.
What are some reasons that family-based communities joined together to form villages. From the sixth through the sixteenth centuries five major factors motivated change in the Western Sudan. The main physical features include the Sahara Desert and the Niger River.
How did location affect the various kingdoms of. West Afica had the advantage of being the closest geographically to the Sahara desert and the wealthy Islamic Empires to the north. The geography impacted where people could live important trade resources such as gold and salt and trade routes that helped different civilizations to interact and develop.
Essentially West Africas farmers and firms produce and trade in highly localized markets and do not achieve the. Africa doesnt have a lot of transportation infrastructure. The weather of Africa was very hot and also humid.
Fun Facts about Ancient Africas Trade Routes. The geography of Africa helped to shape the history and development of the culture and civilizations of Ancient Africa. The earliest communities were made up of families and were farming communities.
It was difficult to trade with people on the other side of the Sahara because it was hard to cross. How did geography affect trade in West Africa. Landlocked areas typically are worse off but there are other geographical disadvantages Africa faces.
Sven Hansche EyeEm Getty Images. To help each other in building cooking and working. This happened because rival African.
Caravans moved at about three miles per hour and it took them 40 days to cross the Sahara Desert. Introduction The motives which brought the people of West Africa into contact with the peoples of North Africa were primarily economic in origin. The region of West Africa includes the southern portion of the bulge of the continent which extends westward to the Atlantic Ocean.
Muslim traders spread Islam throughout Western Africa.
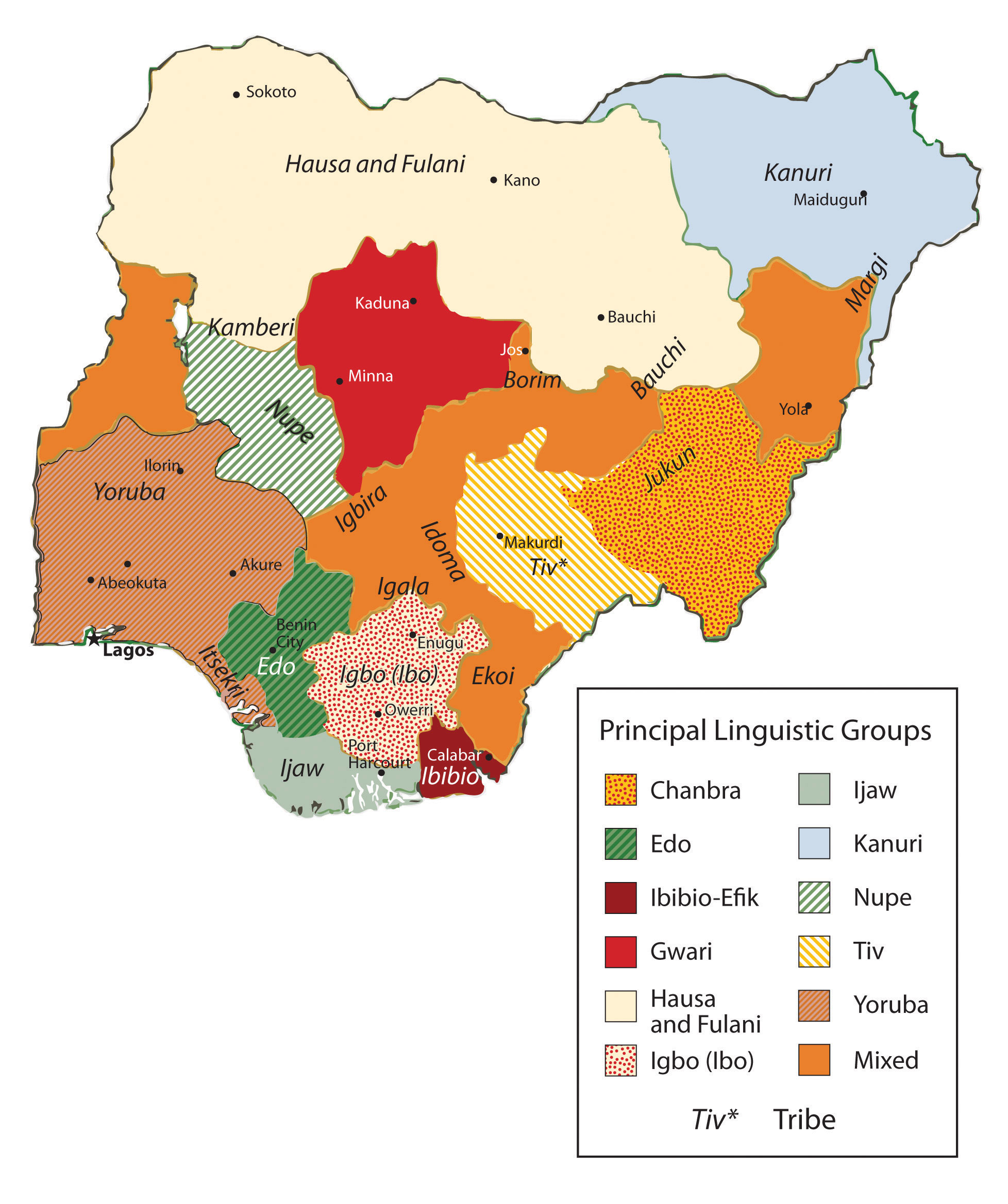
7 3 West Africa World Regional Geography
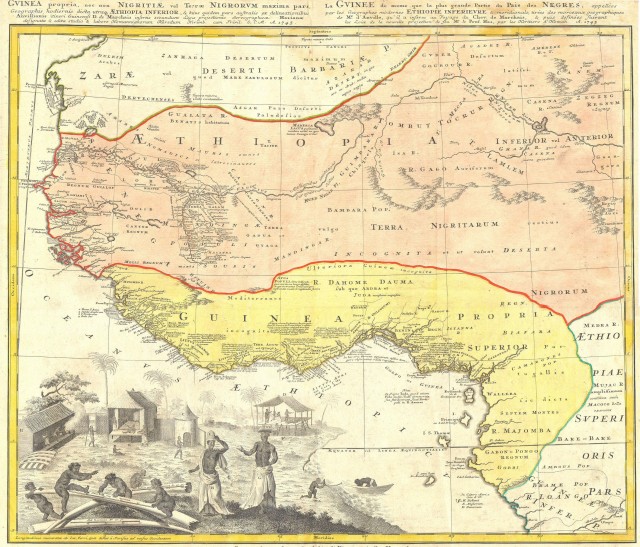
West African Trading Settlements

Ghana Empire Trade Routes Africa African Empires Africa Map

Universal Map World History Wall Maps Africa 1200 1600 Haritalar Cografya Harita

Ancient Africa Trading Activity Social Studies Middle School 7th Grade Social Studies 6th Grade Social Studies
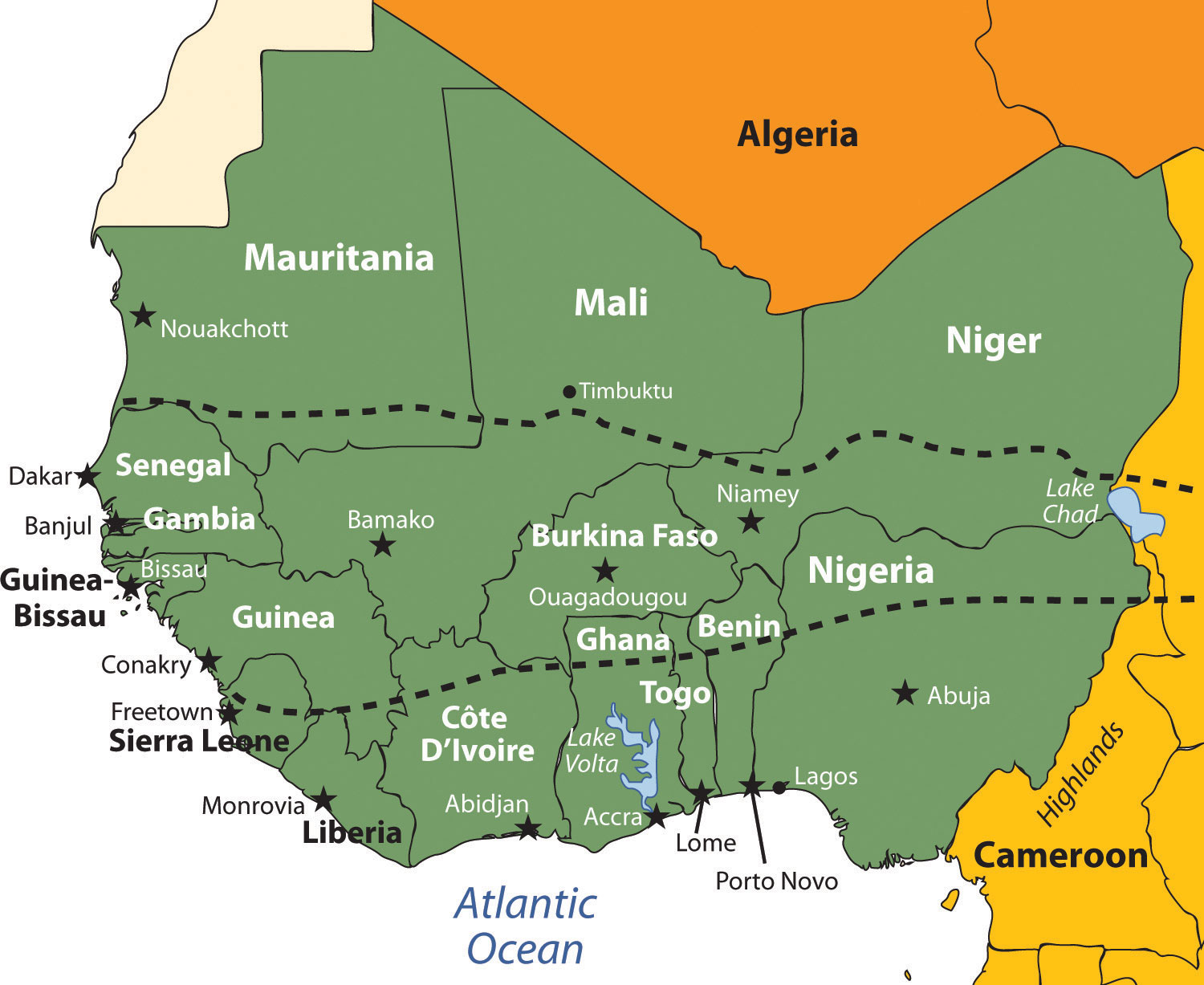
7 3 West Africa World Regional Geography

African Civilizations Interactive Notebook Unit Inb World History Interactive Notebooks Vocabulary Flash Cards Interactive
0 comments
Post a Comment